背景
前不久项目上一段代码出现 crash,因为 dispatch_once 出现死锁问题
出现问题的代码简化后如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| @interface UIDevice (Screen)
- (BOOL)isIPhoneX;
@end
@implementation UIDevice (Screen)
- (BOOL)isIPhoneX {
static BOOL isIPhoneX = NO;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
if (@available(iOS 11.0, *)) {
UIWindow *mainWindow = [UIApplication sharedApplication].windows.firstObject;
BOOL shouldRemoveWindow = NO;
if (!mainWindow) {
mainWindow = [[UIWindow alloc] init];
mainWindow.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor];
shouldRemoveWindow = YES;
}
if (mainWindow.safeAreaInsets.bottom > 0.f) {
isIPhoneX = YES;
}
if (shouldRemoveWindow) {
[mainWindow removeFromSuperview];
}
}
});
return isIPhoneX;
}
@end
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @implementation ViewController
- (BOOL)prefersStatusBarHidden {
if ([[UIDevice currentDevice] isIPhoneX]) {
NSLog(@"do something");
return NO;
}
return YES;
}
@end
|
UIDevice分类方法 -isIPhoneX 内部调用 window 的 safeAreaInsets 属性,会触发当前显示的 ViewController -prefersStatusBarHidden 方法,而 -prefersStatusBarHidden 内部又再次调用了 -isIPhoneX 从而导致 dispatch_once 递归死锁。
dispatch_once 原理
那么 dispatch_once 为什么会递归使用的时候造成死锁呢?
来看看其源码实现 (这里为了简化代码分析,选用libdispatch-339.1.9,项目上 GCD 版本和此版本不一样,但核心逻辑大致相同)
1
2
3
4
5
6
| void
dispatch_once(dispatch_once_t *val, dispatch_block_t block)
{
dispatch_once_f(val, block, _dispatch_Block_invoke(block));
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| struct _dispatch_once_waiter_s {
volatile struct _dispatch_once_waiter_s *volatile dow_next;
_dispatch_thread_semaphore_t dow_sema;
};
#define DISPATCH_ONCE_DONE ((struct _dispatch_once_waiter_s *)~0l)
void
dispatch_once_f(dispatch_once_t *val, void *ctxt, dispatch_function_t func)
{
struct _dispatch_once_waiter_s * volatile *vval =
(struct _dispatch_once_waiter_s**)val;
struct _dispatch_once_waiter_s dow = { NULL, 0 };
struct _dispatch_once_waiter_s *tail, *tmp;
_dispatch_thread_semaphore_t sema;
if (dispatch_atomic_cmpxchg(vval, NULL, &dow, acquire)) {
_dispatch_client_callout(ctxt, func);
dispatch_atomic_maximally_synchronizing_barrier();
tmp = dispatch_atomic_xchg(vval, DISPATCH_ONCE_DONE, relaxed);
tail = &dow;
while (tail != tmp) {
while (!tmp->dow_next) {
dispatch_hardware_pause();
}
sema = tmp->dow_sema;
tmp = (struct _dispatch_once_waiter_s*)tmp->dow_next;
_dispatch_thread_semaphore_signal(sema);
}
} else {
dow.dow_sema = _dispatch_get_thread_semaphore();
tmp = *vval;
for (;;) {
if (tmp == DISPATCH_ONCE_DONE) {
break;
}
if (dispatch_atomic_cmpxchgvw(vval, tmp, &dow, &tmp, release)) {
dow.dow_next = tmp;
_dispatch_thread_semaphore_wait(dow.dow_sema);
break;
}
}
_dispatch_put_thread_semaphore(dow.dow_sema);
}
}
|
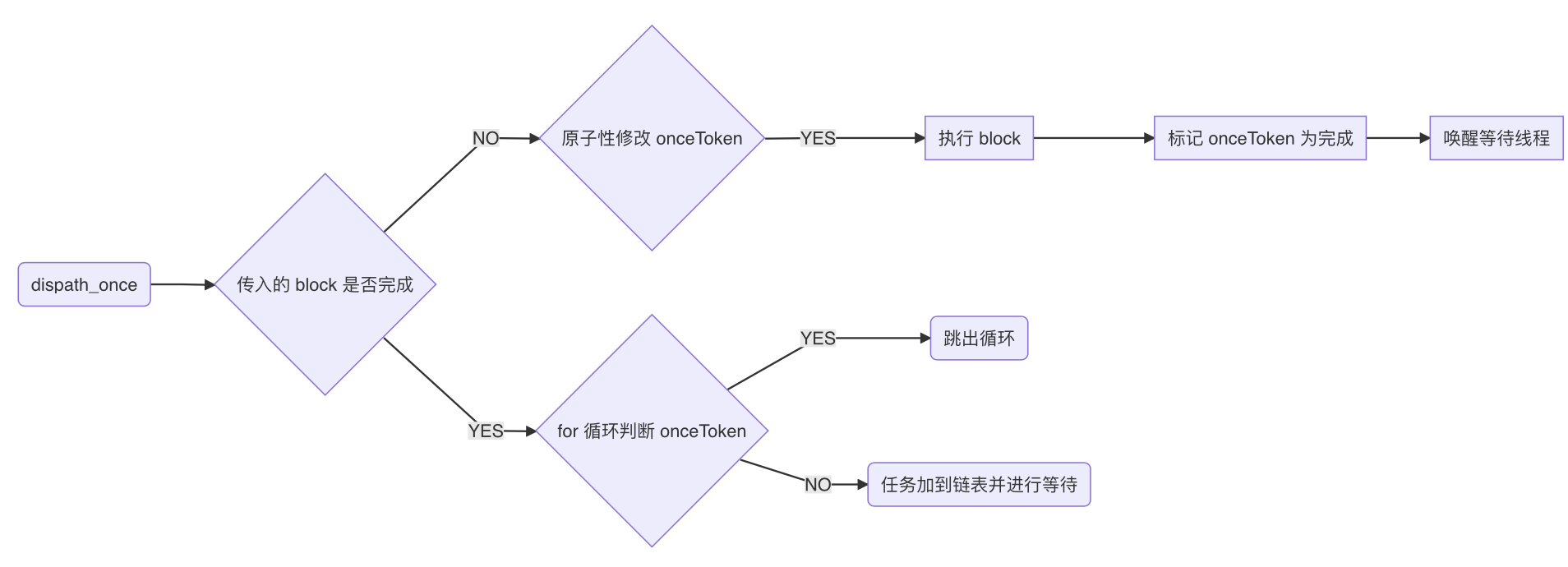
问题原因
- (BOOL)isIPhoneX 方法中 dispatch_once 传入的 block 内部在相同线程递归执行 - (BOOL)isIPhoneX ,导致前一个任务被后一个任务阻塞,后一个任务又依赖于前一个的完成状态,导致死锁
反思
上文的 crash 是从逻辑细节看,因为传入 dispatch_once 的 block 内部递归执行触发同一个 dispatch_once。而从函数设计来看,是因为函数内部逻辑不够单纯,出现了外部依赖。dispatch_once 执行的 block 应该尽可能保持单纯、简单。
对于 - (BOOL)isIPhoneX 这个case 来说,允许极端情况下执行多次内部判断逻辑对性能影响不大,退而求之,可使用静态全局变量保存执行记录;如果遇到极端场景,一开始是并发执行,就允许多次执行完整的判断逻辑,而之后直接使用计算过的结果。这里可以参考QMUI 中判断全面屏的逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| static NSInteger isNotchedScreen = -1;
+ (BOOL)isNotchedScreen {
if (@available(iOS 11, *)) {
if (isNotchedScreen < 0) {
if (@available(iOS 12.0, *)) {
SEL peripheryInsetsSelector = NSSelectorFromString([NSString stringWithFormat:@"_%@%@", @"periphery", @"Insets"]);
UIEdgeInsets peripheryInsets = UIEdgeInsetsZero;
[[UIScreen mainScreen] qmui_performSelector:peripheryInsetsSelector withPrimitiveReturnValue:&peripheryInsets];
if (peripheryInsets.bottom <= 0) {
UIWindow *window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:UIScreen.mainScreen.bounds];
peripheryInsets = window.safeAreaInsets;
if (peripheryInsets.bottom <= 0) {
UIViewController *viewController = [UIViewController new];
window.rootViewController = viewController;
if (CGRectGetMinY(viewController.view.frame) > 20) {
peripheryInsets.bottom = 1;
}
}
}
isNotchedScreen = peripheryInsets.bottom > 0 ? 1 : 0;
} else {
isNotchedScreen = [QMUIHelper is58InchScreen] ? 1 : 0;
}
}
} else {
isNotchedScreen = 0;
}
return isNotchedScreen > 0;
}
|
参考文章
5.44 Built-in functions for atomic memory access
滥用单例之dispatch_once死锁
